High-throughput point-of-care testing using the smartphone-based, cloud computing-enabled ECL analyzer and single ITO electrode-based sensing chips
High-throughput point-of-care testing using the smartphone-based, cloud computing-enabled ECL analyzer and single ITO electrode-based sensing chips
Pan, J. F.#;Zhang, R.F.#; Xia, S. Q.;Yang, M. S.;Jiang, L. L.*;Yi,C. Q.*
Microchemical Journal, 2025
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2025.112707
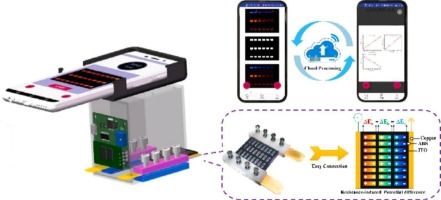
Abstract. High-throughput electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensing in a quantitative manner is becoming one of the most important methods for clinical diagnosis, food safety inspection, environmental surveillance, and etc. This study reports on: 1) a 3D-printed smartphone-based portable ECL analyzer (the SPEA) installed with a self-developed application (the SPEA-App) for precise collection and automatic processing of ECL signals at points-of-needs; and 2) a single-electrode-based and position-resolved ECL sensing chip (the e-chip, 40 mm × 40 mm) containing 24 identical rectangular electrolytic cells for high-throughput ECL sensing assays. Multiplexed quantitation of H2O2, TPrA and dopamine (DA) have been successfully demonstrated using the SPEA integrated with a single e-chip. Noteworthy, the ECL signal processing model is deployed in a Linux server via Python’s Flask backend framework, eliminating the dependence of data-processing capability of smartphones. The applicability and reliability of the SPEA integrated with the e-chips are validated by on-site quantitation of DA in serum samples, which exhibits comparable accuracy to HPLC-MS/MS method. This cost-effective, easy-of-use and versatile smartphone-based sensing system is easily accessible to everyone through the Internet of Things, and can be tailored for diverse applications, enabling high-throughput bioanalysis at anywhere, anytime, and by anyone.

