A tumor microenvironment responsive mesoporous polydopamine theranostic probe embedded with Gd/I-doped carbon nanodots for CT/MR/FL imaging and chemo/photothermal synergistic therapy
A tumor microenvironment responsive mesoporous polydopamine theranostic probe embedded with Gd/I-doped carbon nanodots for CT/MR/FL imaging and chemo/photothermal synergistic therapy
Zhao, J. K.#; Dai, D. S.#; Zhou, L. F.; Yu, Z.; Ma, J. P.; Yang, M.; Yi, C. Q*.
Carbon, 2024
?https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2024.119065
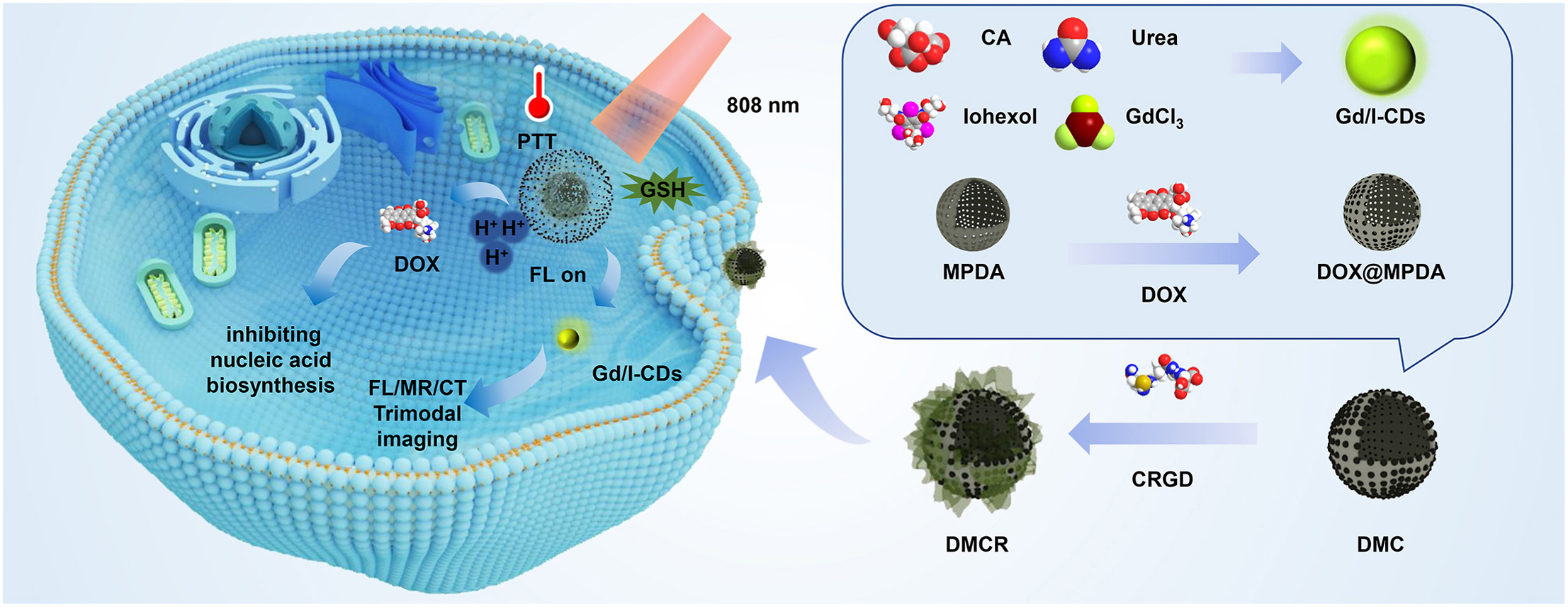
Abstract. This study reports a smart theranostic probe, designated as DMCR, designed for simultaneous CT/MR/FL imaging and chemo/photothermal synergistic therapy. Gd/I-doped carbon nanodots (designed as Gd/I-CDs) are synthesized for the first time using a straightforward one-step solvent thermal approach, serving as the efficient FL/MR/CT trimodal imaging component of DMCR. Subsequently, chemical drug doxorubicin (DOX), diagnostic moiety Gd/I-CDs and tumor-targeting peptide CRGD are successively conjugated onto mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA) to prepare DMCR. Besides its role as versatile scaffold for loading various functional moieties, MPDA serves two additional functions: as an efficient fluorescence quencher for Gd/I-CDs, and an effective photo-sensitizer for photothermal therapy. Therefore, loading DOX into MPDA facilitates the resulting DMCR for chemo/photothermal synergistic tumor therapy. DMCR exhibits excellent water-solubility, biocompatibility, and strong tumor-targeting capability. The decomposition of MPDA by over-expressed glutathione (GSH) and H+ in the tumor microenvironment leads to the GSH/H+-responsive release of diagnostic moieties Gd/I-CDs and therapeutic moieties DOX, triggering the fluorescence turn-on of Gd/I-CDs. In addition, DMCR exhibits a high r1 relaxation rate (38.3 mM−1s−1) and X-ray absorption capability (153.8 Hu mM−1). Both in vitro and in vivo experiments confirm DMCR's high effectiveness in FL/MR/CT triple-modal imaging of tumors and synergistically inhibiting tumor growth with improved efficacy.

