课题组主要研究方向:
1. 生物医学传感技术:基于纳米材料的可控合成与功能化,开发生物医学传感新技术和多元分析新探针,实现复杂样本中和细胞内生化标志物的超灵敏和高特异性检测与成像;
2. 现场快速检测系统:基于智能移动终端和单片机平台,开发高灵敏和高特异的生物医学传感新器件和便携式智能化新仪器,实现复杂样本中生化标志物的原位现场快速检测;
3. 纳米生物材料:从分子到细胞水平研究纳米材料与生物大分子相互作用机理,基于纳米材料的可控合成与功能化,开发诊疗一体化纳米生物新材料用于生物成像和同步治疗。
最新进展
Enzyme-Based Electrochemical Sensing Systems for On-Site Detection: Recent Progress and Prospects
Wang, H. W.; Liu, C.; Feng, T. T.; Zhang, Y. F.; Wu, Y. F.*; Dai, Z.*; Yi, C. Q*.
Small, 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202507926

Abstract. The growing demand for rapid and reliable health monitoring drives significant advancements in enzyme-based electrochemical sensors for point-of-care testing (POCT) applications. This review highlights recent developments in enzyme electrode technology, with a focus on surface modifications, immobilization techniques, and electrode materials that significantly enhance sensor stability, sensitivity, and accuracy in detecting critical health biomarkers. The integration of these electrochemical sensors with portable devices and smart technologies, enabled by innovative hardware and software designs, positions them as highly practical tools for clinical diagnostics and health monitoring. Despite these advances, several challenges persist in ensuring their broad applicability in diverse environments. This review explores these challenges and discusses future research directions. By providing these insights into current innovations and future possibilities, this review aims to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and foster the continued development of enzyme-based electrochemical sensors in healthcare applications.
AIEgen-Based and Smartphone-Assisted On-Site Quantitation of Cystatin C for Monitoring of Chronic Kidney Disease
Xia, S. Q.#; Zhu, X.#; Niu, S. Q.#, Zhang, W. Q.; Gong, J. Y.; Luo, Z. F*.; Li, M. J.* Yi, C. Q*.
Aggregate, 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.70127
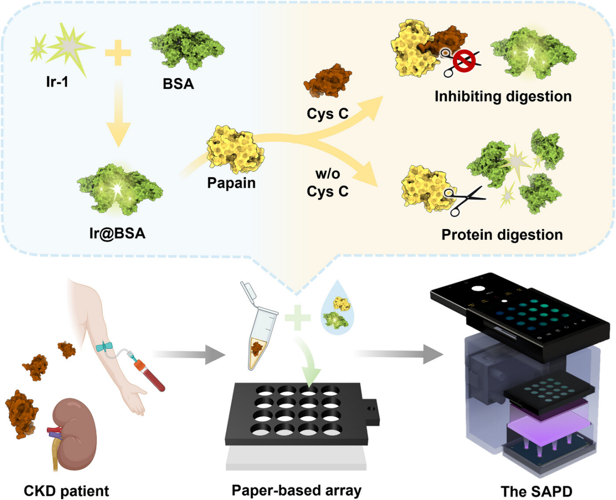
Abstract. The development of affordable and user-friendly diagnostic tools for early warning and monitoring progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is crucial to reducing CKD-related morbidity and mortality. This study reports on (1) a protein-templated AIEgen, Ir@BSA, which emits intense green phosphorescence with a quantum yield up to 69.40% and a lifetime up to 1839.40 ns in aqueous solution; (2) a straightforward protocol for Cys C quantitation, which employs Ir@BSA as the phosphorescent signal indicator and papain as the biomolecular recognition element, respectively; and (3) a smartphone-based portable phosphorescence reader (termed as SAPD), which can stably excite and accurately collect phosphorescence signals from the paper-based arrays. Quantitation of Cys C in clinical serum samples using SAPD integrated with the paper-based arrays highlights its remarkable advantages including high sensitivity (0.36 µg mL−1) and specificity, cost-effectiveness (∼$67.5 per set), portability (∼450 g), good precision (RSD ≤ 8.25 %), good accuracy (comparable to clinical standard latex immune-turbidimetric method), and high throughput (16 samples per experiment). More importantly, this study reveals the significant potential of Cys C as an early warning marker of CKD progression. The reported method enables Cys C quantitation anywhere, anytime, by anyone, and is ideally suited for mass screening for CKD and home monitoring of CKD progression, facilitating early diagnosis and proactive management of CKD.
A Wearable Electro-Controlled Microneedle Device for Synergistic Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy
Chen, S. J.; Chen, F. Q.; Gong, X.; Zhang, B. B.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y. X.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z. P.; Yu, S. D.; Xie, X.; Wei, F. X.; Yang, J. B*.; Yi, C. Q*.; Jiang, L. L*.
Small, 2026
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202508880
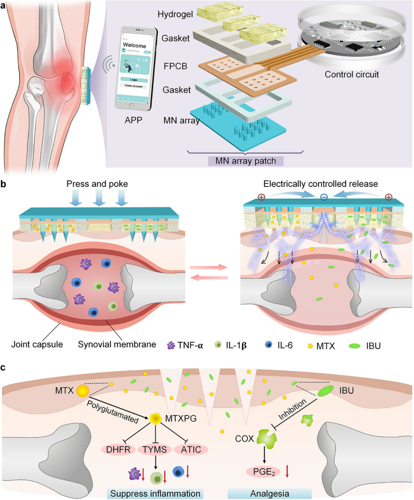
Abstract. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by persistent joint inflammation and pain. Conventional systemic therapies, typically administered orally or by injection, often result in gastrointestinal side effects and poor patient compliance. Although microneedles (MN) enable localized and minimally invasive drug delivery through the skin, their therapeutic efficacy remains limited by uncontrollable and unpredictable release kinetics. Here, this work reports a wearable electro-controlled MN device (EMND) for synergistic RA therapy. The EMND mainly consists of a MN array, a conductive hydrogel, a miniature control circuit and a smartphone-based application. The MN array facilitates transdermal access at the lesion site, while the conductive hydrogel enables electrically triggered, on-demand drug release via iontophoresis. This design allows precise spatiotemporal control of multiple therapeutics to achieve synergistic anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. In RA rat models, EMND treatment reduced inflammatory cytokine levels to 11.38%–14.51% of baseline and increased pain thresholds by 5.24-fold. Overall, this wearable EMND offers an exciting prospect for facilitating RA treatments and autonomy of therapeutic interventions, with potential applications for other chronic conditions.
Point-of-Care Testing for Abnormal Amino Acid Metabolism: Visualized Colorimetric Detection of Tryptophan Based on Au@MnO2 Nanoparticles
Huang, Y.; Zhuang, X. T.; Zhang, R. Y.; Yu, Q. H.; Kuang, Z. W.; Qiu, C. B.; Luo, Z. F.; Rong, M. C*.
Journal of Analysis and Testing, 2025
https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-025-00381-y
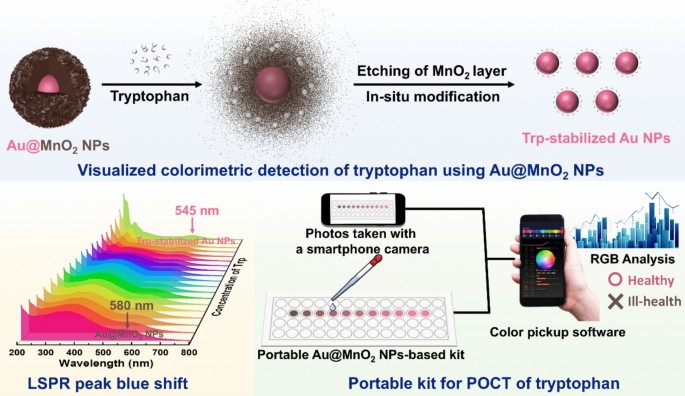
Abstract. In this study, a novel colorimetric detection method for tryptophan is developed using Au@MnO2 NPs based on their redox reaction. Tryptophan etches the outer MnO2 NPs shell and forms a stable protective layer outside the released Au NPs core in situ, accompanied by a noticeable color change from brown to pink. According to the absorbance ratio of 545 nm and 580 nm (A545/A580), a rapid (within 1 min), accurate, and specific detection method for tryptophan is constructed amidst other common amino acids. Coupling with a smartphone application, integrated Au@MnO2 NPs-based portable test strips can be used for the point-of-care testing (POCT) of tryptophan.
A Magnetically Actuated Neural Probe for Multi-Focal Location in Epilepsy
Wang, C.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Xie, X.; Yi,C. Q.* ; Jiang, L. L.*
Advanced Materials Technologies, 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202500308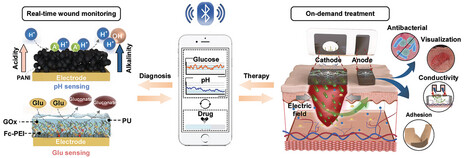
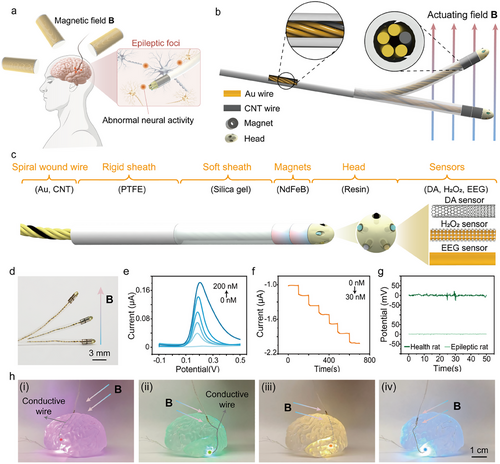
Abstract. Intractable epilepsy often requires the use of stereo-electroencephalography (SEEG) for localizing the epileptic focus. However, SEEG is associated with high invasiveness and relatively limited localization accuracy. This study presents a novel magnetically actuated neural probe (MANP) that integrates remote magnetic navigation and multimodal sensing capabilities to achieve precise localization of epileptic foci. MANP can controllably navigate and accurately target the potential regions of epileptic foci through a single surgical microhole under magnetic actuation. Equipped with multimodal biosensors, MANP tracks EEG signals and neurotransmitter levels (dopamine and hydrogen peroxide) in real-time, providing detailed insights into abnormal brain activities. In vivo experiments with epileptic rats, MANP detected elevated levels of dopamine and hydrogen peroxide alongside high-frequency (4–30 kHz) EEG signals at seizure onset. It effectively identifies multiple suspicious lesions via a single skull entry point under magnetic navigation, distinguishing epileptic from normal brain regions. Therefore, MANP enables minimal invasion, remote magnetic navigation, multi-modal detection, and multi-focal localization, providing a versatile platform for the precise localization of epileptic foci and potential treatment of other neurological disorders.